Brief:
EUS Diagnosis, and Endotherapy in a case of Recurrent Acute Pancreatitis (RAP)
Description:
A 38 yrs male patient was referred to evaluate the exact etiology of recurrent episodes of acute pancreatitis since last few years (> 5 episodes). So far all imaging studies have been inconclusive.
-
EUS revealed normal CBD and gall bladder.
-
MPD appeared dilated (4.5 mm) in the head region with prepapillary narrowing of the MPD and dilated side branches.
-
A small stone and few concrements were seen in the prepapillary portion of the MPD.
-
Abnormal course of MPD was noted in the head region which raises suspicion of incomplete divisum.
-
MPD appeared undilated and irregular in the genu and body. No evidence of any hypoechoic lesion in the pancreas. No evidence of any pseudocyst or nodes.
-
Selective cannulation of MPD
-
Pancreatogram showed ‘S’ shaped MPD with incomplete divium.
-
Major papilla sphincterotomy was performed after a 3 fr stent was placed through the major papilla and prepapillary stone was seen exuding out of Minor papilla which was delivered with minor papilla sphincterotomy
TAKE HOME MESSAGE
This case shows us the importance of detailed mapping of Pancreas with EUS followed by a definitive endoscopic treatment of Recurrent Acute Pancreatitis leading to chronic pancreatitis. It is always a challenge to perform any Endotherapy in undilated pancreatic duct, but as we have shown here, that if the centre has adequate EUS and ERCP experience then such patients can be managed successfully. It is imperative to keep in mind that post Endotherapy pancreatitis chances are high in undilated ducts and therefore the above mentioned procedure should be performed only by highly trained experts in an infrastructure to deal with small duct interventions, especially equipment and accessories. So it is my appeal to all practicing clinicians that please do not disregard a patient saying that nothing can be done for recurrent acute pancreatitis.
Image:
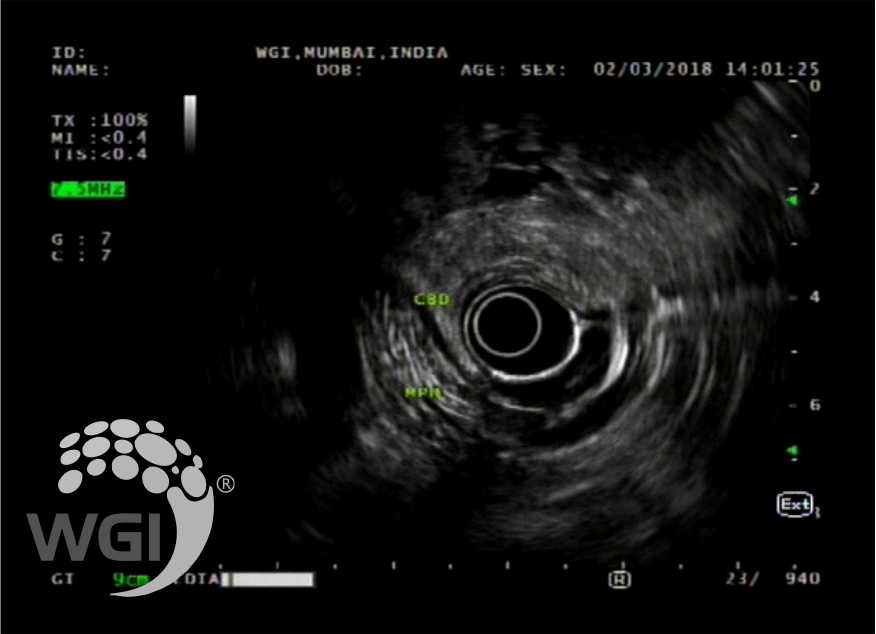
1. EUS revealed normal CBD and gall bladder
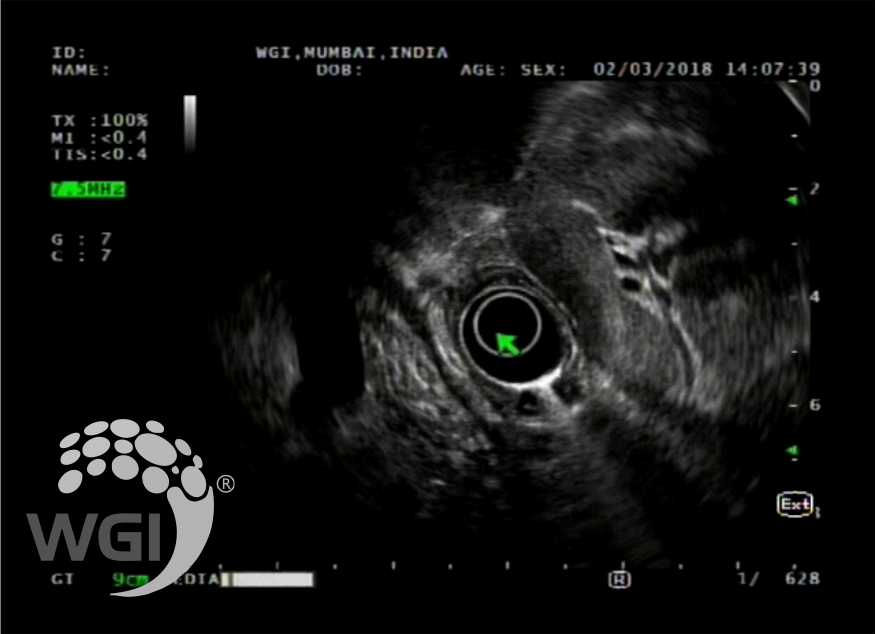
2. A small stone and few concrements were seen in the prepapillary portion of the MPD.
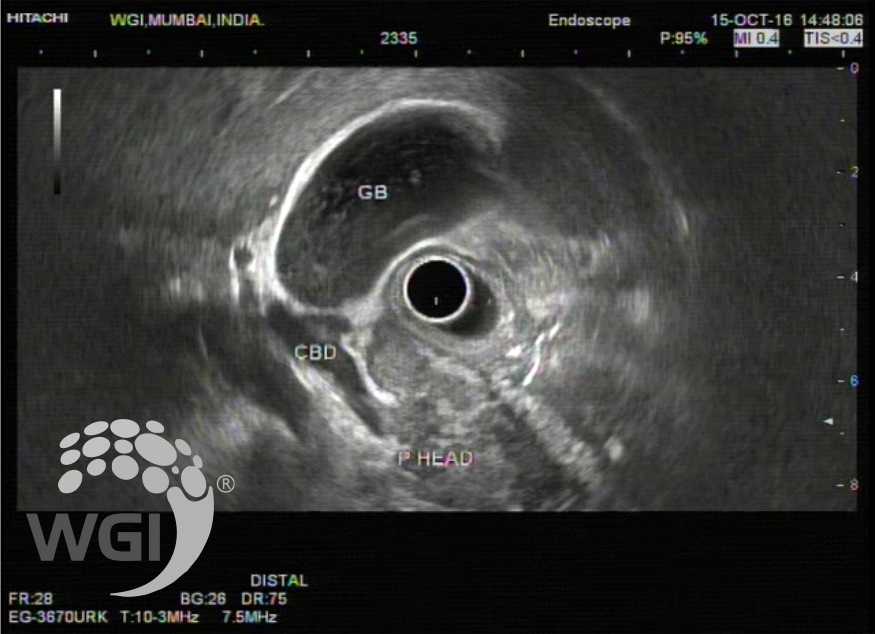
3. MPD appeared dilated and irregular in the genu and body.
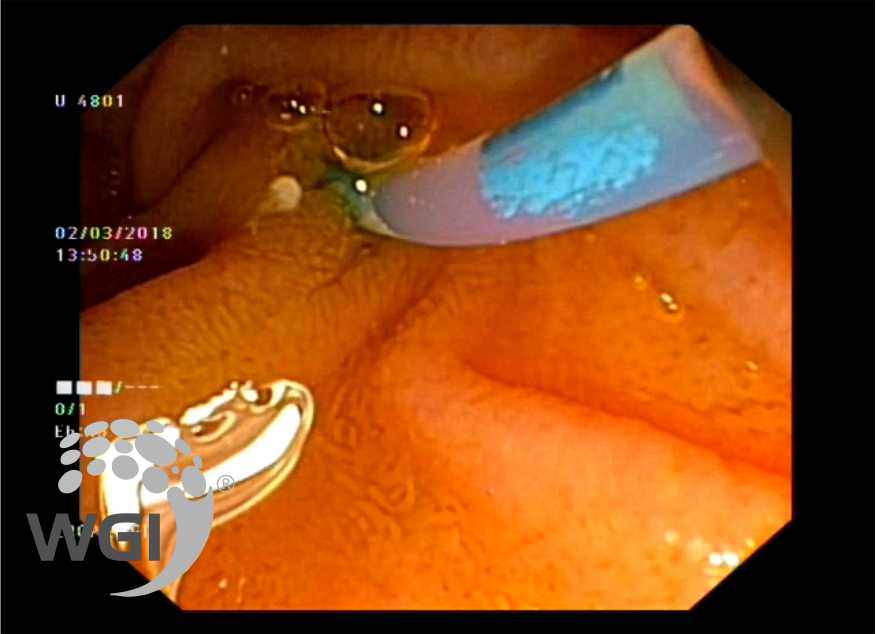
4. Selective cannulation of MPD
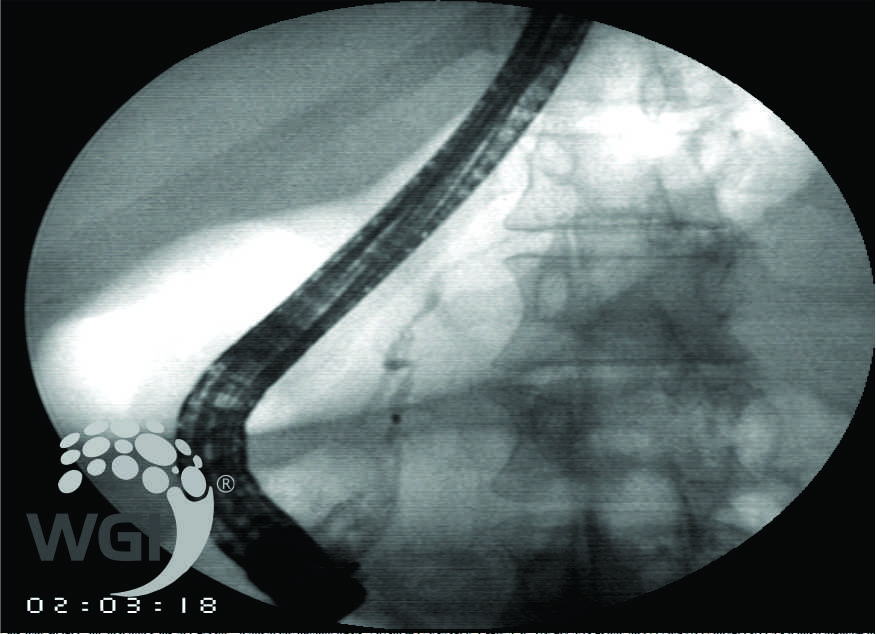
5. Pancreatogram showed ‘S’ shaped MPD with incomplete divium.
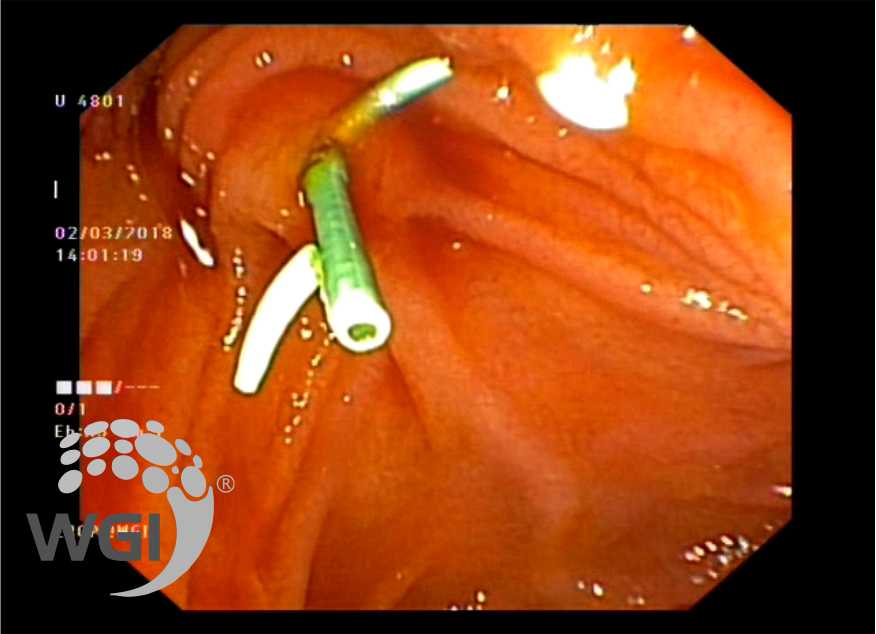
6. A 3 fr stent was then placed and prepapillary stone seen exuding out of minor papilla
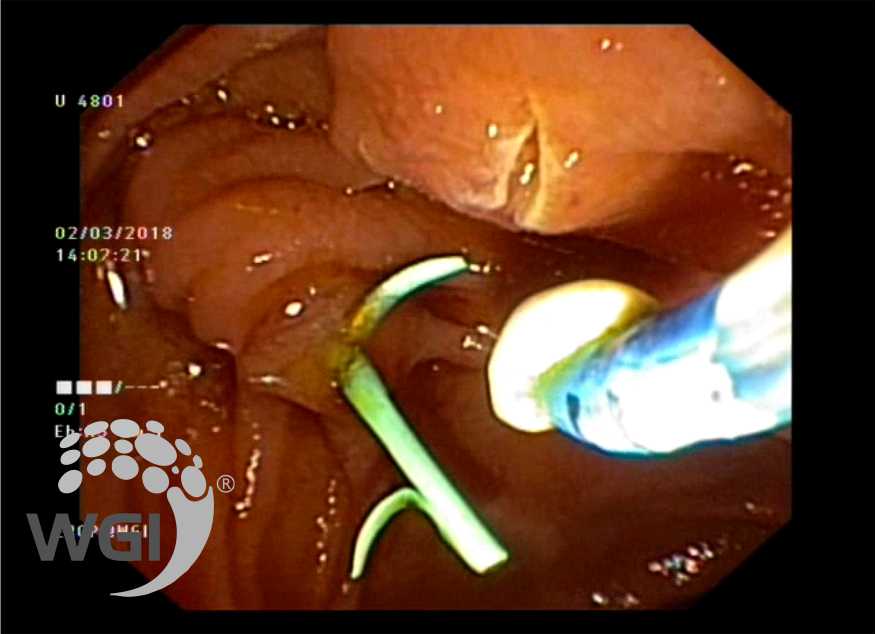
7. Minor papilla sphincterotomy performed.
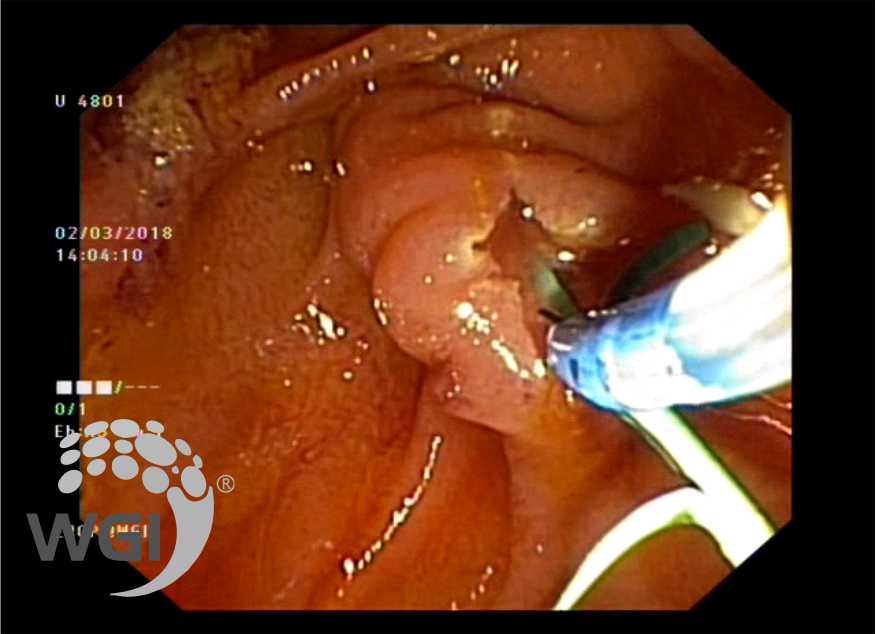
8. Major papilla sphincterotomy performed.
Posted by Dr. Vipulroy Rathod
Feb 27, 2019
Categories:
Gastrovision Case Capsules
© Endoscopy Asia